How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to stunning aerial photography, videography, and even professional applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding its components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced maneuvers and ensuring responsible flight practices. We’ll explore everything from basic controls to advanced techniques, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
This comprehensive guide covers all aspects of drone operation, providing a structured learning path for beginners and valuable insights for experienced pilots. We will explore the various types of drones available, their functionalities, and the importance of adhering to safety regulations and ethical considerations. Each section is designed to be clear, concise, and practical, enabling you to quickly grasp the concepts and apply them to your own drone flights.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the function of each major part, highlighting differences in quality and price across various models.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated work of several key components. These include the propellers, motors, flight controller, battery, GPS, and camera.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, hover, and move. Higher-quality propellers are typically more durable and efficient, resulting in longer flight times and smoother operation.
- Motors: These convert electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to spin the propellers. Brushless motors are generally preferred for their efficiency and longevity compared to brushed motors.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this component receives input from various sensors and uses algorithms to maintain stability and execute flight commands. Higher-end flight controllers often offer more advanced features and better stability.
- Battery: Provides the power for all drone components. Battery capacity (mAh) directly impacts flight time. Higher-capacity batteries offer longer flight times but are typically more expensive and heavier.
- GPS: A Global Positioning System module allows the drone to pinpoint its location, enabling features like return-to-home (RTH) and precise waypoint navigation. Higher-quality GPS modules offer improved accuracy and reliability.
- Camera: Captures photos and videos. Camera quality varies significantly based on sensor size, resolution, and features like image stabilization. Higher-end cameras typically offer better image quality and more advanced features.
Drone Component Price and Quality Differences
The price of drone components reflects their quality and performance. Generally, higher-priced components offer improved durability, efficiency, and features. For example, a higher-quality flight controller will provide more stable flight and better responsiveness, while a higher-resolution camera will produce sharper images and videos. Similarly, more powerful motors will enable faster speeds and more agile maneuvers. However, higher quality often translates to increased weight, which can impact flight time and maneuverability.
Comparison of Three Drone Models
| Model | Camera Resolution | Flight Time (approx.) | Price (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone Model A (Budget) | 12MP | 15 minutes | $300 |
| Drone Model B (Mid-range) | 48MP | 25 minutes | $600 |
| Drone Model C (High-end) | 6K Video | 35 minutes | $1200 |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is essential to ensure safe and responsible operation. This includes checking the drone’s components, battery level, and surrounding environment. Understanding emergency procedures and legal regulations is equally important.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Verify the GPS signal is strong and accurate.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check the propellers for damage or looseness.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Confirm you are flying in a legal and safe airspace.
- Inform others of your flight plan.
Emergency Procedures
In the event of a malfunction or loss of control, it’s crucial to know how to react quickly and safely. This might involve engaging the return-to-home (RTH) function, attempting a controlled landing, or preparing for a potential crash.
- Loss of Control: Immediately attempt to regain control using the emergency stop function if available. If unsuccessful, prepare for a controlled crash by trying to guide the drone to a safe landing zone.
- Battery Failure: Initiate the RTH function immediately. If the RTH fails, attempt a controlled emergency landing.
- GPS Failure: Switch to a lower-risk flight mode, such as Attitude mode, and manually control the drone back to a safe location.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly involves adhering to all applicable laws and regulations. These regulations vary by country and region, and it’s crucial to research and understand the specific rules before flying. Ethical considerations include respecting privacy, avoiding sensitive areas, and being mindful of the environment.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and efficient takeoff and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents. This section Artikels a step-by-step guide for beginners and discusses variations for different environments.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedure
- Pre-flight checks: Ensure all pre-flight checks are complete.
- Find a safe location: Choose an open area away from obstacles and people.
- Power on the drone and controller: Ensure both are connected.
- Calibrate the drone: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for compass and IMU calibration.
- Initiate takeoff: Gently lift the drone using the throttle control. Maintain a slow and steady ascent.
- Hover: Practice hovering at a safe height before moving the drone.
- Landing: Slowly lower the drone to the ground, maintaining control of the throttle. Power off the drone and controller.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques in Various Environments
Different environments require adjustments to the standard takeoff and landing procedures. For example, in windy conditions, a more sheltered location may be necessary, and the pilot should compensate for wind gusts. In urban areas, extra caution is needed to avoid obstacles and ensure compliance with local regulations. Near water, the risk of drone loss increases, so additional safety measures might be needed.
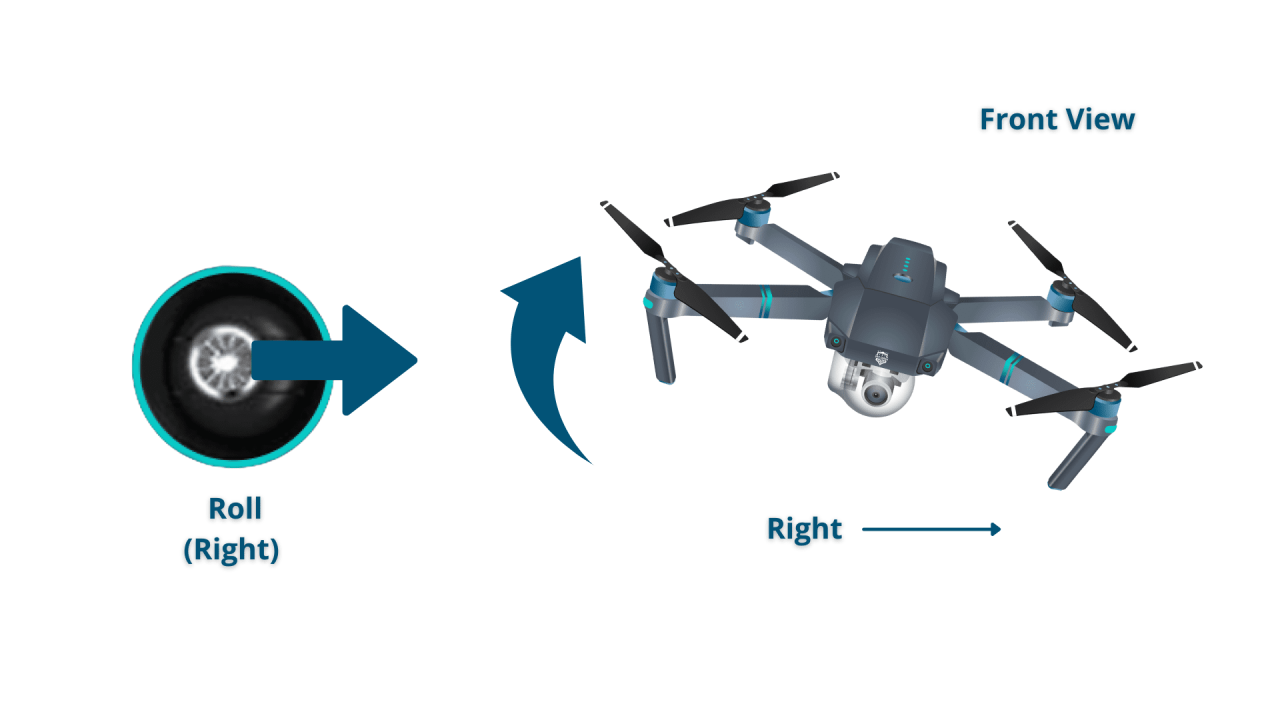
Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Mastering drone flight controls is essential for safe and effective operation. This section explains how to control altitude, direction, and speed, along with tips for smooth movements and common maneuvers.
Controlling Altitude, Direction, and Speed

Most drone controllers use a combination of joysticks and buttons to control the drone’s movement. One joystick typically controls the drone’s altitude and yaw (rotation), while the other controls the drone’s forward/backward and left/right movement. The speed is often adjustable through settings on the controller or within the drone’s app.
Tips for Smooth and Precise Movements
Smooth and precise drone movements are crucial for capturing high-quality footage and avoiding accidents. This requires practice and a gentle touch on the controls. Avoid sudden movements, and learn to use small, incremental adjustments to control the drone’s position and orientation.
Common Drone Maneuvers
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Forward/Backward/Left/Right Movement: Moving the drone in the desired direction.
- Yaw: Rotating the drone left or right.
- Ascent/Descent: Changing the drone’s altitude.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding your drone’s camera features and settings is essential for capturing high-quality photos and videos. This section explains how to adjust settings for optimal image quality in various lighting conditions and how to utilize different camera modes.
Drone Camera Features and Settings
Typical drone cameras offer a range of features and settings, including resolution, ISO, shutter speed, aperture (if adjustable), and white balance. Understanding how each setting affects the final image is crucial for achieving the desired results.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Image Quality
The optimal camera settings depend on the lighting conditions. In bright sunlight, a lower ISO and faster shutter speed may be needed to prevent overexposure. In low-light conditions, a higher ISO and slower shutter speed might be necessary to capture sufficient light. White balance should be adjusted to ensure accurate color reproduction.
Using Different Camera Modes
- Photo Mode: Captures still images.
- Video Mode: Records moving footage.
- Timelapse Mode: Captures a series of images over time, which can be compiled into a time-lapse video.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance is vital for keeping your drone in optimal working condition and extending its lifespan. This section Artikels a routine maintenance schedule and provides solutions for common drone problems.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include inspecting the drone for physical damage, cleaning the propellers and camera lens, checking the battery health, and lubricating moving parts as needed. The frequency of maintenance will depend on the drone’s usage.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Common problems include battery issues, motor malfunctions, GPS signal loss, and camera malfunctions. Troubleshooting these problems often involves checking connections, replacing faulty components, or updating the drone’s firmware.
Flowchart for Diagnosing and Resolving Typical Drone Malfunctions

A flowchart can provide a structured approach to troubleshooting. It would start with identifying the problem (e.g., drone won’t start, GPS signal lost), then guide the user through a series of checks and potential solutions, leading to a resolution or the need for professional repair.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Once you’ve mastered basic drone operation, you can explore advanced maneuvers and flight modes to enhance your skills and capture more creative footage.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of the regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently and safely take to the skies with your drone.
Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips, rolls, and 360-degree rotations, require a good understanding of drone controls and a comfortable level of skill. These maneuvers should only be attempted in a safe and open environment, away from obstacles and people.
Flight Modes
- GPS Mode: Relies on GPS signals for positioning and stability.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to its starting position, regardless of GPS signal.
Creating Professional-Quality Aerial Footage
Creating professional-quality aerial footage requires careful planning, smooth drone operation, and post-processing. This involves selecting appropriate locations, using appropriate camera settings, and employing editing techniques to enhance the final product.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available online; for comprehensive instructions, check out this helpful guide on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation, ultimately enhancing your aerial experience.
Drone Battery Management
Proper battery care and charging procedures are essential for maximizing battery lifespan and ensuring safe operation. This section covers battery care, signs of failure, and a comparison of different battery types.
Importance of Proper Battery Care
Proper battery care involves storing batteries in a cool, dry place, avoiding overcharging or deep discharging, and using the correct charger. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for battery care will significantly extend the battery’s lifespan.
Signs of a Failing Drone Battery
Signs of a failing drone battery include reduced flight time, increased charging time, and unusual heating during charging or use. A failing battery should be replaced to prevent unexpected power loss during flight.
Comparison of Different Battery Types
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Flight Time (approx.) | Charging Time (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo Battery A | 1500 mAh | 20 minutes | 60 minutes |
| LiPo Battery B | 3000 mAh | 40 minutes | 120 minutes |
| LiPo Battery C | 4500 mAh | 60 minutes | 180 minutes |
Drone Software and Apps
Drone software and apps provide essential tools for controlling the drone, adjusting settings, and reviewing captured footage. This section explores the functionality of common drone apps.
Functionality of Common Drone Software Applications, How to operate a drone
Drone apps typically offer features such as live video feed, flight controls, camera settings adjustments, flight path planning, and photo/video management. The specific features vary depending on the drone model and the app.
Comparison of Different Drone Apps
Several apps are available for iOS and Android devices, each offering different features and user interfaces. Some apps might offer advanced features like obstacle avoidance or automated flight modes, while others focus on simplicity and ease of use.
Connecting the Drone to a Smartphone or Tablet
Connecting a drone to a smartphone or tablet usually involves enabling Wi-Fi or Bluetooth on both devices and following the instructions in the drone’s app. The connection process is typically straightforward but might vary slightly depending on the drone model and app.
Flying Drones in Different Environments
Flying drones in various environments presents unique challenges and requires adapting flight techniques and safety procedures. This section discusses the considerations for flying in different conditions.
Challenges and Considerations of Flying Drones in Various Environments
Windy conditions can make it difficult to control the drone’s stability, while urban areas present obstacles and potential hazards. Flying near water increases the risk of losing the drone if it crashes or malfunctions. Each environment requires careful planning and risk assessment.
Best Practices for Flying Drones Safely in Different Environments
Best practices include choosing appropriate flight modes, adjusting flight speed and altitude to account for environmental conditions, and always maintaining visual line of sight with the drone.
Safety Precautions in Challenging Conditions
- Windy Conditions: Avoid flying in strong winds, choose a sheltered location, and use appropriate flight modes.
- Urban Areas: Be aware of obstacles, comply with airspace regulations, and avoid flying near crowds.
- Near Water: Have a backup plan in case the drone falls into the water, and consider using flotation devices.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that blends technology, skill, and responsible practice. From the initial thrill of takeoff to the precision of capturing breathtaking aerial footage, the experience is both exhilarating and empowering. By understanding the fundamentals of drone technology, safety procedures, and legal considerations Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently explore the exciting world of aerial flight, capturing stunning visuals and expanding your creative possibilities.
Remember, responsible drone operation is paramount; always prioritize safety and adhere to all applicable regulations.
Q&A
What is the maximum flight time for most consumer drones?
Flight time varies greatly depending on the drone model and battery size, typically ranging from 15 to 30 minutes.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and regulations.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately attempt to regain control using the emergency stop function if available. If unsuccessful, prioritize safety and allow the drone to land itself or descend gradually. Report the incident to the relevant authorities.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially in areas with magnetic interference.
